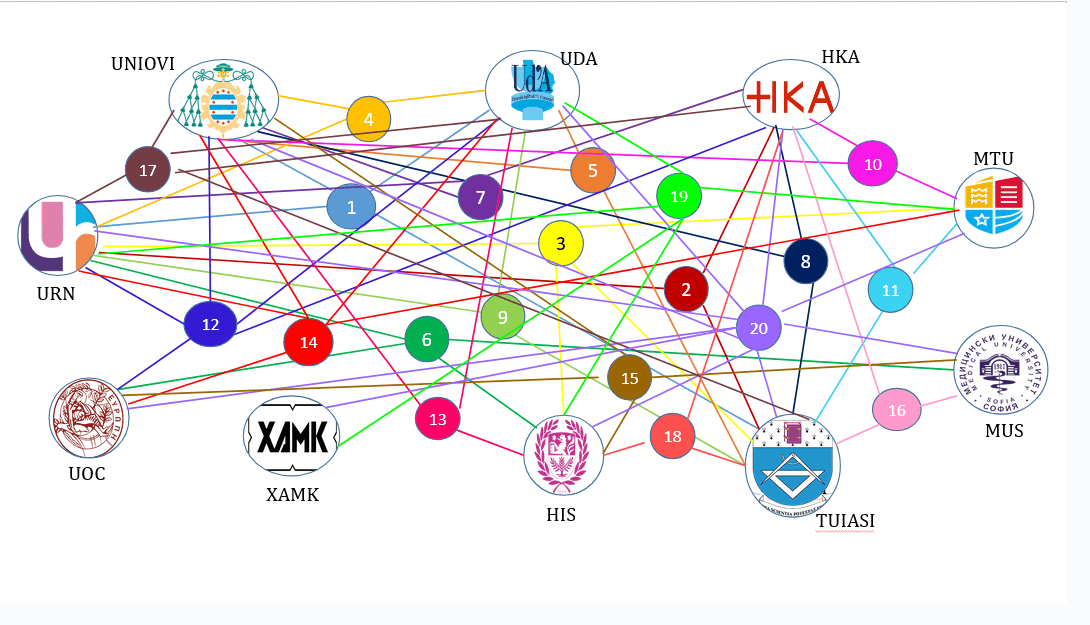
Results of the first Call for INGENIUM Research Groups 2024
Faculty and research staff of the INGENIUM Universities (UNIOVI – ES, MUS – BG, UoC – EL, HKA – DE, XAMK – FI, Ud’A – IT, HiS – SE, MTU – IE, URN – FR and TUIASI – RO) were invited to submit proposals for the creation and early development of INGENIUM joint research groups or new collaborative research projects. The aim of the initiative is to support innovative research and encourage new cooperation between INGENIUM’s partners.
In this process, faculty and research staff from INGENIUM universities used CONNECT (https://connect.unich.it/), a specialized research matching platform developed at Ud’A, to identify and connect with potential partners. Each proposal has been developed by a research team consisting of members from at least three INGENIUM universities.
Applications have closed and a total number of 20 projects have been selected:
1. Reliability and Survival Analysis of Multi-State Random Systems: Theory and Applications
Brief description of the project:
Project objectives: Research on complex systems has rapidly expanded in the last two decades and today spans diverse fields: mathematics, physics, economics, and biology, to name a few. The purpose of this research project (RP) is to study the reliability of a complex system and to prepare a set of responses based on the development of new stochastic models and statistical techniques. The investigation considers an integrated approach to the problem based on new concepts from different disciplines, such as probabilistic models, statistical analyses, decision theory, and their applications.
This RP focuses on the achievement of the next main objectives:
- the development of suitable stochastic models for the macro-description of a complex system;
- study of the interactions among the components of the system and their impact on the macrodynamics;
- advancement of new reliability metrics for the system;
- assessing ad hoc statistical techniques for the estimation of the models’ parameters;
- incorporating uncertainty in terms of fuzzy variables;
- executing real applications in economics, finance, energy and biology.
Planned activities:
The RP’s development requires specific activities that can be summarized in the following phases:
- “Literature review and organizational aspects”;
- “Identification of theoretical problems, real applications, data acquisition, and data analysis”;
- “Development of new mathematical models and their fuzzy modifications”;
- “Estimation and inferential analysis; forecasting of the systems”;
- “Execution of real application to problems identified in Phase 2”;
- “Discussion of the results and possible future developments in relation to large grants”
Expected results:
The expected results concern both theoretical and applied aspects. Theoretical ones pertain to the development of new theorems about the system behavior and its mathematical properties. The applied results concern the understanding of specific systems which arise when studying real problems from economics, finance and biological systems.
Institutions involved:
- UDA
- UNIOVI
- URN
- TUIASI
2. Valorisation of biomass and Safes Productions
Brief description of the project:
The Biomass valorisation is one of the strategies for developing energy/chemical sectors in accordance with European sustainable development policy. The development and use of chemical or biological processes require good understanding of transformation and purification operations. In the case where the reactions release heat, the development of safe reactors is also necessary to avoid accidents in dense geographical area involving industrial activities.
This project aims to identify process valorisation routes and propose multidisciplinary research axes between 3 research teams specialized respectively in the development: TUIASI – biological processes; Univ. Rouen – chemical processes; Karlsruhe Univ. – automation and Instrumentation of reactors. To successfully initiate a network with effective long-term connections, the activities will be aimed at knowing each structure at the human and material level and on research themes around biomass. The identification of similarities between different colleagues involved in this project will be sought before opening up to other research structures in the medium term. In this project, the discovery of the structure and the activities of the researchers will be planned with priority given to visit each research structure and the environment around the university. For each University, organization and participation in scientific events, either internal to the laboratory (seminar) or external are some examples of actions associated with this project. This scientific meeting will also be a way to communicate around the Ingenium project.
A Midterm, these exchanges could lead to more concrete actions via collaboration on current research projects (for instance student exchanges (thesis and master’s degree) via the Erasmus program) to strengthen links. These actions would favor the response to European project calling on the valorization of biomass, in particular those identified in connection with Horizon Europe.
Institutions involved:
- URN
- TUIASI
- HKA
3. Achieving Internationalisation through best practice in Modern Foreign Language and Intercultural Communication pedagogies
Brief description of the project:
In the context of higher education, the term “internationalisation” refers to the integration of an international, intercultural, or global perspective into both the curriculum and the process of teaching and learning. At the undergraduate and postgraduate levels, the effective teaching of foreign languages is crucial for achieving what Wachter (2003) some years ago, termed “internationalisation at home.” This concept encompasses both crosscultural communication and proficiency in foreign languages.
The objective of this project is to enable a cross-collaborative sharing of expertise as well the initiation of research proposals to enhance students’ language proficiency as a means of implementing “internationalisation at home”. Another important focus of this research group is looking at best practice at each other’s institutions in relation to internationalisation at home, i.e. provision of language /intercultural courses and the recognition of internationalisation at home by staff and students. Each partner will have a clearly defined role in relation to the sharing of best practice.
Planned activities:
- To investigate and share diverse expertise and needs among the team;
- To form focus groups in each institution with all relevant stakeholders and investigate best practice examples in the university and wider communities;
- To undertake a literature review on published research that interrogates both the theoretical and practical synergies between effective language pedagogy, intercultural matters and internationalisation in third level contexts;
- To establish pathways for small scale research studies and therein investigate research funding opportunities;
- To promote more public engagement with the wider university community in a range of disciplines through conducting an audit of need for graduates with FL proficiency and intercultural/internationalisation awareness.
Expected Results:
- Extensive literature review of published research on the theoretical and practical synergies between effective language pedagogy, intercultural matters and internationalisation in third level contexts;
- Compilation of best practice policies and pedagogies, resulting from focus group discussions as collaborative sharing;
- Creation of framework for implementation of best practice in “internationalisation at home” in the universities participating in the INGENIUM network alliance.
Institutions involved:
- URN,
- HIS,
- TUIASI,
- MTU
4. Effectiveness of Integrative Intervention Strategies for Binge Eating in Patients with Overweight or Obesity: A multidisciplinary Approach
Brief description of the project:
Project objectives:
The main goal of the BE-side project is to compare the short- and long-term outcomes of three 12-week interventions among outpatients with overweight/obesity and binge eating (BE):
- treatment-as-usual for weight loss (TAU);
- combined TAU and guided self-help for improving eating behaviors (TAU+GSH);
- combined TAU, GSH, and biofeedback (TAU+GSH+BF).
The primary outcomes will be self-reported reduction of days with objective BE episodes (OBEs).
The secondary outcomes will be impulsivity, emotion dysregulation, interoceptive awareness, distress, physiological correlates of arousal (skin conductance and heart rate variability), and inflammatory biomarkers.
Additionally, the cost-effectiveness of treatments will be evaluated.
Planned activities:
- Recruitment.
A consecutive sample of sixty treatment-seeking outpatients with overweight/obesity enrolled at the Clinical Nutrition Centre of the University Hospital of Chieti (Italy) will be recruited from referrals to a dietary control program for any medical reason. Screening will be conducted by experienced physicians and psychologists.
- Screening
Inclusion criteria: (1) age 18-65 years; (2) BMI≥25 kg/m2; (3) ability to read and write in Italian; (4) Binge Eating Disorder (BED) or subthreshold BED status. Exclusion criteria: (1) current treatment for BE with a registered psychologist; (2) severe psychiatric disorders; (4) cognitive impairment; (5) pregnancy; (6) severe medical comorbidity.
- Assessment Psychological assessment.
Psychophysiological assessment. Inflammatory biomarkers assessment.
- Randomization
Patients who met inclusion will be randomly assigned to: (1) TAU, (2) TAU+GSH, (3) TAU+GSH+BF.
- Re-test
12-week follow-up-1
4-month follow-up-2 (after the end-of-treatment)
- Data Analysis
- Dissemination
Expected results:
The TAU+GSH arm is expected to be comparable to the TAU+GSH+BF arm in reducing the number of days with OBEs but is expected to be significantly less effective in improving secondary outcomes (impulsivity, emotional dysregulation, interoceptive awareness, distress, physiological inflammatory markers). The TAU arm is expected to show significant inferiority regarding the primary and secondary outcomes and cost-effectiveness compared to the TAU+GSH and TAU+GSH+BF conditions.
Institutions involved:
- UDA
- UNIOVI
- URN
5. Unraveling Neurodegeneration: Innovative Therapeutic Discoveries through Brain Organoid Models
Brief description of the project:
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) pose significant risks to human health by interfering with hormonal function. These chemicals, present in everyday products, leach into the environment and contaminate food sources, exposing humans to their harmful effects. Of particular concern is their potential impact on neurodevelopment and neurodegenerative diseases. Despite regulatory efforts by the European Commission to limit exposure, EDCs persist in the environment, causing socioeconomic burdens and health issues.
This project aims to elucidate the neurotoxic effects of EDCs using advanced in vitro models, including human- induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neurons and brain organoids. Through interdisciplinary approaches involving high-content microscopy, mitochondrial function analysis, and investigation of blood-brain barrier permeability, the project seeks to understand the mechanisms underlying EDC-induced neurotoxicity and identify potential mitigating agents.
The outcomes of this research will provide crucial insights into the impact of EDCs on the human nervous system, informing regulatory decision-makers and guiding the development of safer consumer products. Dissemination efforts targeting policymakers, healthcare providers, and the general population will raise awareness of the health and environmental risks associated with EDC exposure, promoting sustainable practices, and supporting stronger regulations.
To ensure the project’s sustainability and impact, a collaborative framework will be established among INGENIUM research partners, facilitating future funding opportunities and stakeholder engagement. By leveraging diverse expertise and cutting-edge techniques, this project aims to create a strong network between the involved universities and deliver robust scientific findings with significant implications for public health and environmental conservation.
Institutions involved:
- UDA
- UNIOVI
- TUIASI
6. INGENIUM Rare Neurogenetic Disease Initiative
Brief description of the project:
Background:
Rare diseases pose a significant healthcare challenge, with millions of these patients remaining undiagnosed or diagnosed after several years. Even if finally successful, this lengthy diagnostic process not only burdens patients and strains healthcare systems but also impedes access to specific treatments. Omics technologies offer promise in expediting diagnosis, yet variation in data interpretation hinders progress. Furthermore, the lack of accurate genetic diagnosis creates obstacles in research efforts to understand the pathophysiology of these rare diseases and ultimately develop novel treatments.
Aims:
Addressing these diagnostic and research obstacles, our INGENIUM Rare Neurogenetic Disease Initiative (Ingenium- RNDI) aims to improve molecular diagnosis of undiagnosed patients by exchanging regionally developed genomic analysis pipelines and experience.
Method of implementation:
Groups involved in our Ingenium-RNDI project include the Zaganas group (University of Crete, Greece), the Nicolas group (University of Rouen, France), the Tajsharghi Group (University of Skövde, Sweden), and the Kaneva/Jordaneva group (University of Sofia, Bulgaria). Our groups jointly form a multidisciplinary team approaching rare neurogenetic disorders from various angles. Employing innovative commercial and in-house solutions, diverse cohorts of undiagnosed cases will be analyzed jointly by us. In addition, we will collaborate with experts in other rare diseases, such as renal, gastrointestinal, and endocrine disorders. This extended multidisciplinary team will focus on specific rare disease subsets, enhancing diagnostic accuracy. Through collaborative research, a consensus on a high-yield diagnostic strategy will be achieved, enhancing knowledge diffusion and capacity building. Student and researcher exchanges between Ingenium-RNDI partners will augment collaboration.
Expected results:
Expected outcomes include expedited and accurate diagnostic protocols. Establishing these unified genomic interpretation approaches will enhance diagnostic accuracy and molecular diagnosis rates, improving healthcare access. In the future, the Ingenium-RNDI aims to secure larger EU funding for rare disease research, establishing enduring collaborations and contributing to sustainable advancements in rare disease diagnosis and treatment.
Institutions involved:
- URN
- UOC
- HIS
- MUS
7. Semantic Interoperability of Biomedical Data
Brief description of the project:
One of the main challenges in the biomedical world is finding mechanisms to integrate heterogeneous data from different sources. Semantic technologies enable this kind of interoperability by means of linked data, shared vocabularies and ontologies.
In this project, we are planning to extend our previous research combining neuro-symbolic technologies like knowledge graphs, ontologies, federated machine learning, and large language models, in order to facilitate the automatic interoperability of biomedical data as well as improving the quality and alignment of this data while respecting data privacy.
The project will consist of establishing new collaboration lines between the three research groups that participate in the proposal, as well as assessing other collaboration lines with other research groups that could be interested in these topics.
Planned activities:
- 3 face-to-face between the three Ingenium partners of the SIBiDA project.
- One workshop on the topic affiliated to an EU Conference or at a local institution to disseminate the common advances of this proposal as well as invite other potential partners from the Ingenium alliance or from other universities.
- Start the preparation of a common European project proposal
- Prepare a joint position paper about the current project which could be submitted to some related international conferences (e.g.,SWAT4HCLS, ISWC, ESWC, etc).
Expected results:
- Establish new joint research lines between the groups involved in this proposal
- Define use cases where semantic interoperability can improve existing solutions
- Analyze the integration of existing biomedical data at different levels like clinical records, ontologies and databases
- Define hybrid approaches that combine machine learning, large language models and ontologies
- Explore the application distributed, peer-to-peer techniques in this domain which also preserve privacy
- Analyze possible applications to other domains like agriculture and nutrition.
Institutions involved:
- UNIOVI
- URN
- HKA
8. Design-for-X of a powertrain for efficient and low-cost electric traction
Brief description of the project:
Project objectives:
In the current context with an emphasis on electromobility, the project addresses the current challenges in the automotive industry on their transition towards the domination of electric vehicles. The purpose of the project is to lay the conceptual foundations and make proof-of-concept laboratory validations of a new powertrain for electric vehicles, increasing the efficiency and power density of electric motors, avoiding rare and expensive materials (magnets). The use of alternative materials is considered, in innovative configurations (multiphase) that will increase the fault tolerance fence and reduce the load on the associated inverters. Recyclability plus life-cycle environmental impact aspects need to be considered, aiming at the best compromise with other performance parameters to reach the stated outcomes.
Planned activities:
The planned activities correspond to TRL2 (Technology concept formulated) and TRL3 (Proof-of-Concept Demonstrated, Analytically), as follows: – Design and investigation of a new parallel hybrid excitation synchronous motor (PHESM) according to the latest EV powertrain requests; FEM based multi-physics model and optimal design (TUIASI, OVIEDO) – Design and investigation of the wide speed-range control structure and algorithms for optimal operation of the designed PHESM (TUIASI) – Integration of the new HESM powertrain into a simulation environment which contains both the component models and a vehicle dynamics model (HKA) – Performance assessment through extension of the simulation environment by a model for interaction, consisting of a traffic and visual simulation of the environment (HKA) – Identification and assessment of the possible new and affordable materials suited for integration in the EV powertrains. Recyclability (OVIEDO) – Dissemination – Identifying the possibilities of continuing and expanding the collaboration.
Expected results:
– A close to e-mobility use of PHESM electric power train for light and medium HEVs and EVs applications; – Publications (Premium Journals or Conferences); – Strategy to continue the research collaboration beyond the funding period.
Institutions involved:
- UNIOVI
- TUIASI
- HKA
9. Regenerative Engineering and Advanced Lab-cultures for Music Tissues
Brief description of the project:
Project objectives:
The project aims to explore the regenerative properties of human muscle stem cells using advanced scaffold materials made from 3D printed biopolymers to create a 3D culture environment.
The planned activities include:
WP1 – designing and testing a bioink comprised of natural and synthetic polymers (polysaccharide derivatives (double bonds grafted compounds) and/or synthetic polymers), followed by the fabrication of muscle cell scaffolds through UV curing or chemical crosslinking;
WP2 – Evaluation of the bioinks on the Axo A3 bioprinter will assess biocompatibility (ISO 10993) and cell adhesion, with subsequent analysis of cell morphology using immunostaining and SEM. Additionally, 3D printing will create grooved cell-culture supporting surfaces to guide myocyte alignment;
WP3 – Human muscle stem cells will then be inserted into the scaffolds for 3D culture, with proliferation rates and myogenesis assessed through various techniques including immunocytochemistry and electron microscopy.
Electron microscopy will help describe the cell grafting, spreading, confluence and alignment on the scaffold. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) collected from the 3D cultures will be analyzed, and functionalized exosomes will be used to stimulate the cultures to evaluate potential positive or therapeutic effects.
Expected outcomes
Include bioinks with appropriate viscosity, sterile cell culture supports characterized by topological specificity (Ra, rigidity, hydrophobicity,..), and innovative platforms for studying muscle cell development and regeneration from stem cells to differentiated myotubes.
Institutions involved:
- UDA
- URN
- TUIASI
10. Innovative Industry Internships with INGENIUM
Brief description of the project:
There are three key objectives for this proposal
- Enhance the competitiveness of each university nationally and globally while simultaneously enhancing the competitiveness of the INGENIUM consortium.
- Enhance the work placement learner experience and professional identity development associated with it through a redesigned and digitally innovative assessment and feedback experience.
- Strengthen external relationships with work placement host organisations through a redesigned and digitally innovative assessment and feedback experience.
The above are the long-term objectives for this body of work. In the first phase described in this proposal, the current work placement assessment and feedback practice along with the student experience will be explored across the three partners. Initial research by MTU revealed the assessment process supports the development of critical graduate attributes but that students are less satisfied with some other aspects e.g. workload, relevance of assessment, assessment challenge (O’Mahony, Murphy & O’Sullivan, 2024). The proposal will support exploring, identifying and sharing of European best practice to enhance assessments potential to shape learning while on work-placement. This will have impact under the three objectives outlined above by building on best practice relationships with host organisations, incorporating best practice in assessment and feedback on placement and by supporting assessment and feedback best practice by host organisations.
In Phase Two, the results of the survey and the case studies will be the basis for a body of work to redesign the assessment and feedback experience of students and host organisation on placement. The redesign process will employ design thinking tools with stakeholders such as service blueprinting, personas and customer journey mapping. This will pave the way for Phase Three , the digital innovation and transformation stage. A possible outcome from this stage could be an app to manage the interactions between all three parties possibly including reflections, assessment, grading, feedback and logistics.
Institutions involved:
- UNIOVI
- MTU
- HKA
11. Brain-Computer Interfaces for ambulatory neuro-rehabilitation
Brief description of the project:
The BCI-REHAB consortium, comprised of INGENIUM and EU partners, focuses on addressing neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and post-stroke conditions. These disorders have widespread implications for individuals and society. Currently, pharmaceutical interventions can only slow cognitive decline. The project aims to develop a personalized rehabilitation program targeting memory, attention, spatial orientation, and motor skills.
The program employs video games with varying difficulty levels, cognitive challenges, and incentives, encouraging patients to adjust their EEG brain signals for progress and rewards. The ultimate goal is to create a comprehensive project concept and proposal for submission to relevant EU calls.
Project objectives (within the INGENIUM Joint Research Group Proposals):
O1: To strengthen the cooperation within the INGENIUM consortium by interconnecting research groups with complementary expertise on a proposed research theme;
O2: To find other relevant expertise among EU research groups enhancing the chance to propose and receive EU funds for a submitted proposal within a suitable EU call.
O3. To identify the most suitable EU call and to submit a proposal.
Planned activities:
1.Revise and assess the state-of-the-art in the frame of the proposed research ideas (O1; Deliverable: Main results integrated in the first video report, month-M3).
2.Bringing together the necessary expertise within the BCI-REHAB consortium; At least one session of relevant research show cases (e.g. on BCI- Federated Learning) at each BCI-REHAB partner’s facilities (O1, O2; dissemination within INGENIUM consortium; Identify additional appropriate partners to address any potential gaps in expertise: e.g. EU partners search portal; participation at an info day relevant to an identified EU call (M8-M11). Deliverable: Report with a list of partners with their relevant expertise and expected contribution; Milestone: The main partners of the BCI-REHAB consortium have been enlisted: M6).
3.Submission of at least one grant proposal for an appropriate EU funding opportunity (O3; organization of: on-line sessions; working visits to the partners’ research facilities; workshops: HKA (M2-M3); EPE2024 Conference (October 2024) organized by TUIASI (M5); Milestone: first release of a draft EU proposal-M10; Deliverables: final proposal for a suitable EU research call – M13; Showcases of the effectiveness of the collaboration between INGENIUM partners – Second Video Report: M13; Scientific joint publication-M11).
Expected results:
1.A strong partnership, made up of INGENIUM&EU partners, with a strong focus on submitting a project proposal within the EU project calls (M6).
2.A number of young researchers already integrated into a research group and familiar with the partners’ research equipment and facilities (M13);
3.Two project video reports (M3, M13);
4.A project proposal ready to be submitted within a suitable EU project call (M13).
Institutions involved:
- TUIASI
- MTU
- HKA
12. Executive functions and creativity in primary school children: International assessment-intervention protocol for the integrating movement and digital technology
Brief description of the project:
The primary objective of this project is to inform all professionals (e.g., teachers, psychologists, educators) about current ecological assessment and empowerment of Executive functions (EFs) and creativity in primary school children with and without Special Education Needs (SEN). In particular, the project is aimed to scope the interdisciplinary fields of psychology, education, and movement sciences and examine the current needs and available strategies incorporating movement and technologies in the assessment and/or strengthening of EFs and creativity. Professionals will be provided with tools and knowledge required to support and enhance these vital capacities in children, ultimately contributing to their holistic development and future success as adults. Our multidisciplinary team, spanning across EU countries, will conduct literature reviews, craft surveys, and facilitated focus groups involving teachers, psychologists, educators, and experts regarding the pivotal role played by EFs and creativity in primary school. The project activities encompass a blend of online and offline meetings designed for the effective implementation of the project, and the participation to conferences and congresses as dissemination strategy.
Anticipated outcomes include (1) detailed reviews of the state-of-the-art on the assessment and strengthening of EFs and creativity in primary school children, with and without SEN, and (2) valuable insights and data gathered from surveys and focus groups involving professionals to get a deeper understanding of the current practices, challenges, and needs in EFs and creativity empowerment in elementary school (3) establishing a solid knowledge base for seeking additional means to support further research on identified issues. Furthermore, the project findings could contribute significantly to the fields of psychology, education, and movement sciences, potentially leading to improved best practices and better outcomes for primary school children and providing directions for future research in this area.
Institutions involved:
- UDA
- UNIOVI
- URN
- UOC
13. Enhancing the Digital Inclusivity of Cultural and Natural Heritage
Brief description of the project:
Project objectives:
The project aims to define and test, theoretically and experimentally, original interdisciplinary knowledge design frameworks, models, and solutions to enhance the digital inclusivity of cultural and natural heritage sites so that all visitors can access and enjoy them regardless their psychophysical or cultural (dis)abilities.
Specific project objectives are:
- To identify strategic aspects concerning the digital inclusivity of heritage sides from a multidisciplinary perspective.
- To share knowledge and best practices, facilitating a comprehensive and culturally diverse approach to the digital inclusivity of heritage sites.
- To jointly propose and test an interdisciplinary knowledge framework to enhance the digital inclusivity of cultural and natural heritage (e.g.: inclusive design principles).
- To promote knowledge exchange and cross-cultural understanding of inclusive heritage sites.
Planned activities:
The project is articulated into three main activities:
- Knowledge production comprising literature review, case study analysis, etc.
- Joint production of a knowledge framework for enhancing the digital inclusivity of cultural and natural heritage sites, comprising a) open tools; b) inclusive design strategies and guidelines; c) effective storytelling techniques; d) digital models for inclusive visit experiences.
- Test and validation of the interdisciplinary knowledge framework, comprising a) selection of site to test the knowledge framework; b) development of inclusive design concepts, with assessment and evaluations; c) final refinement and validation of the framework.
Expected results:
An open access publication containing project results will be produced. It will contain:
- Relevant research data about the inclusivity of heritage sites.
- The interdisciplinary knowledge framework for the digital inclusivity of cultural and natural heritage, jointly developed and tested on real case studies.
- Qualitative evidence on the enhanced inclusivity of heritage sites, made through joint efforts, documenting positive impacts on visitors’ experiences, and broadening the target audience base.
- Open documentations, digital tools, and working materials for future projects.
- Strengthened international cooperation between partnering institutions, providing a solid foundation for future joint initiatives.
Institutions involved:
- UDA
- UNIOVI
- HIS
14. Illuminating Drug Discovery
Brief description of the project:
The initial step in drug discovery is the identification of successful lead candidates. For higher chances of clinical success, it is crucial to have a large high-quality screening collection of unique compounds. These requirements have challenged researchers to develop innovative strategies to rapidly generate collections of structurally complex molecules for screening. LIGHT-UP aims at providing innovative solutions for modern drug discovery by exploiting the powerful tools offered by light-based technology to rapidly generate molecules that may be relevant to human health in an environmentally friendly manner. LIGHT-UP will leverage the diverse expertise within the five participant institutions of the INGENIUM alliance, ensuring the achievement of the objective proposed.
For achieving the proposed goals, LIGHT-UP is articulated in four work packages: WP1 (Excellence), dedicated to the scientific coordination, including the organization of meetings/workshops; WP2 (Training), devoted to the implementation of training activities, including a training school; WP3 (Communication, Dissemination, Exploitation), in charge of the elaboration and implementation of the general Communication and Dissemination Work Plan including the creation of the visual identity, webpage and dissemination materials; WP4 (Project sustainability/development) devoted to identifying routes to ensure the continuity, sustainability and longevity of the established collaboration, analyzing possible sources of funding and coordinating the preparation of proposals. LIGHT-UP will increase the size of the libraries of potentially bioactive compounds that may be relevant to human health while decreasing the carbon footprint of the Drug Discovery process. In addition, the researchers involved in the research will benefit from a multidisciplinary environment, crucial for training the next generation of researchers that European industry and academia require for the upcoming drug R&D challenges. In line with the Sustainable Development goals, the project will “improve health and education and spur economic growth, all while tackling climate change and working to preserve our oceans and forests”.
Institutions involved:
- UDA
- UNIOVI
- URN
- UOC
- MTU
15. Why the herd effect alters the health
Brief description of the project:
Project objective:
To understand the herd effect, a phenomenon by which individuals follow the behavior of others rather than deciding independently, and its relevance to health behavior.
Planned activities:
Literature review to provide conceptualization of the herd effect and its relevance to health behaviors; exploration of the impact of the herd effect on health behaviors using a mixed-methods approach (qualitative study, survey-based quantitative study and qualitative comparative analysis).
Expected results:
Conceptualize the herd effect and its relevance on health behaviors; recommendations for future research and practice; social impact through contact with stakeholders in health and social care and media engagement.
Institutions involved:
- UNIOVI
- UOC
- HIS
- MUS
16. Robotic-Enhanced Balance Rehabilitation System
Brief description of the project:
The project aims to forge a pioneering collaboration among multidisciplinary academic teams within the Ingenium alliance and industrial partners to develop an innovative system for diagnosing, rehabilitating, and training individuals with vestibular disorders. By aligning our efforts with SMART criteria, we ensure our contributions to vestibular rehabilitation are impactful and driven by a synergy of advanced engineering and medical research.
Our core objective is to enhance collaboration across research groups and universities, improving both theoretical and practical approaches to mental health and the judicious use of technology. This initiative sets the stage for ambitious, cross-cultural, and interdisciplinary projects beyond this venture.
Planned Activities:
- Organizing initial meetings to outline the team’s objectives and framework.
- Assigning specific roles and responsibilities within the team.
- Creating a robust technology infrastructure and communication network for the group.
- Developing a comprehensive database of research resources and expertise.
- Conducting thorough literature reviews on vestibular rehabilitation’s societal impact.
- Gathering quantitative and qualitative insights from medical staff and patients to inform our approach.
- Drafting research proposals based on identified needs and existing academic work.
- Developing conceptual models and integrating these proposals into the broader project.
- Establishing a detailed system design and simulation framework. Expected Outcomes:
- Enhanced understanding of how digital technology, AI, and robotics can revolutionize vestibular diagnostics and therapy.
- Creating a valuable dataset for training AI algorithms to assist diagnosis and rehabilitation.
- The formation of a cross-academic database enriched with insights from medical professionals and patients.
- Development of a simulation model to explore various diagnostic and rehabilitation scenarios for vestibular disorders.
- Establishment of a dedicated research group to address future challenges in health and wellbeing.
This project aims to advance vestibular rehabilitation and foster a sustainable environment for future research and development in health technology.
Institutions involved:
- TUIASI
- MUS
- HKA
17. Upcycling of wastes and by-products to green chemicals and energy
Brief description of the project:
Objectives:
Our objective is to upcycle CO2 and agro-industrial wastes (lignin) into valuable chemicals (methanol/aromatics/hydrogen) for energy/industry purposes, aligning with the EU’s goal (2050, carbon-neutrality). This goal involves developing CO2-capture-and-storage(CCS), alongside sustainable fuels.
We’ll elaborate, as sorbents, functional materials, based on biopolymers and ionic-liquids(ILs), and even aqueous- amino-acids-(K/Li/Na)-salts(AAAS), alternatives in chemisorption to traditional (toxic, volatiles, oxidizable) alkanolamines. New sorbents should absorb/release CO2 with mild pressure/temperature realizing CO2 gravimetric yield, superior/comparable to the current systems.
Metal biopolymers-embedded-nanoparticles will be prepared to photochemically convert captured-CO2 into methanol.
We’ll investigate electrochemical coupled production of anodic-generated peroxides and cathodic-generated hydrogen. We’ll employ hydrogen for CO2 reduction and peroxides for lignin selective depolymerization and biobased-platform-chemicals production.
Alternative energy-sources constitute a challenge to democratic governance transforming society into a central agent of the process. Raising citizens participation in public affairs and public awareness and understanding are essential. Adequate comprehension of public perceptions leads to effective communication and education strategies, democratic policies, socially strengthened technologies.
Activities:
URN:
-Synthesis/Characterization of reactive, polymerizable ILs;
-Elaboration/Characterization of membranes based on poly(vinyl alcohol) and poly(lactic acid) with immobilized-ILs. HKA:
-Electrochemical processes for coupled production (cathodic-hydrogen/anodic-peroxides) in undivided-batch-cell;
-Lignin depolymerization;
-Simultaneously CCS/wastewater-treatment with AAAS;
-Smart sensor integration. UdA:
-Nanophotocatalysts synthesis/characterization/test for CO2 photoreduction;
-Membrane sorbents physical-chemical characterization/test. TUIASI:
-CCS by AAAS;
-Environmental-assessment. UdO:
-Academic literature/multi-country studies review on energy/climate-change perception;
-Eurobarometer datasets analysis.
Results:
Creation of European research network about integrated process to upcycle wastes into valuable products, from the emissions to chemical valorization and dissemination.
-Ecosustainable CCS materials,based on waste/cheap;
-Green routes for lignins/CO2 valorization;
-Green photocatalysts;
-Scalable electrochemical setup/protocol for peroxides/hydrogen production;
-Conceptualization of “climate culture” model (knowledge, attitudes, values, engagement, public-participation);
-Comparative analysis on energy-sources public perceptions;
-Planned applications for joint grants (ERC, Horizon, COST);
-Joint PhD/masters thesis, visiting researchers/professors, for network enhancement/continuation;
-Enlargement to excellence research centers, even not-INGENIUM.
Institutions involved:
- UDA
- UNIOVI
- URN
- TUIASI
- HKA
18. Circular and Sustainable Innovations for a future Bioeconomy
Brief description of the project:
The quest for sustainability is one of INGENIUM’s core themes and main objectives. These efforts could greatly benefit from a strengthening of research activities in this field, but the competencies are widely spread across universities and disciplines. The project aims to systematically identify these research competences and interests and to establish a corresponding interdisciplinary joint research group within INGENIUM around the topic of Circular and Sustainable Innovations to accelerate the transition towards a future Bioeconomy. The outcome of the project should lead to several project proposals including INGENIUM partners and beyond by accessing the broader network of partners
In order to successfully implement a joint research group as described, the following approach will be pursued. (1) Before collecting and structuring the information on the current status, it is proposed to first develop a framework for categorization and a questionnaire that could be sent to the partners (Workpackage WP1: Framework & Questionnaire). This could facilitate the collection and evaluation of data, which will be collected and evaluated among the alliance partners in WP2: Data Collection & Evaluation. In parallel, appropriate calls at European level will be identified to facilitate the forming of tailored consortia (WP3: Collection of Target Calls). To initiate and strengthen cooperation, an (online)-networking event will be organized to present the results of WP2 and WP3 and showcase selected initiatives of INGENIUM groups. This networking event will be the kick-off for a dedicated joint research group (WP4: Networking Event & Research Group Initiation). After this initial networking event, joint proposal writing will be encouraged and facilitated with the aim of elaborating several proposals and establishing long-term cooperation between the partners (WP5: Proposal Compilation). The whole project will be accompanied by the necessary project management (WP6: Project Management).
Institutions involved:
- HIS
- TUIASI
- HKA
19. Empowering Recovery in Mental Health Difficulties (Physical Activity, Nutrition, Digital Tech)
Brief description of the project:
Treatment and care in mental health recovery remains a global crisis, with morbidity and mortality rates far behind the general population. There have been repeated calls from international agencies and experts to reframe the care paradigm.
This requires moving from a medical model to a human rights approach that recognises lifestyle factors and the social determinants of health. This partnership will examine physical activity, nutrition, and digital technology as evidence-based mechanisms to transform practice and help close the mortality gradient.
Aclú-EU builds on the work of the Ingenium partners to accelerate progress and deliver multidisciplinary solutions.
Institutions involved:
- UDA
- URN
- XAMK
- HIS
- MTU
20. Multidisciplinary Approach to Research Integrity and Ethics
Brief description of the project:
Project objectives:
INGENIUM unites ten universities, mandating a steadfast commitment to elevated research integrity (RI) and research ethics (RE) across all levels. This project aims to strategically convene INGENIUM’s stakeholders, fostering the exchange and implementation of good practices in RI and RE.
Planned activities:
The multidisciplinary collaborative effort aims to produce an official INGENIUM declaration on RI and RE, slated for unveiling at a hybrid colloquium event in May 2025 in Munster Technological University. To realise the strategic intent of MARIE, project team members will meet on a monthly basis online to discuss and progress the project, with short-term strategic milestones in place to sustain its acceleration and continued progress.
Expected results:
In parallel with the declaration, the project’s intention is to provide a framework to implementing the values outlined in the declaration, utilising MARIE’s members’ collective multidisciplinary knowledge of RI/RE implementation to further embed good research practices – including current developments such as the ethical use of artificial intelligence (AI) and ethical co-authorship practices – with cognisance of international cultural developments and debates surrounding RI and RE. The declaration and framework would thus solidify INGENIUM’s role at the forefront of RI and RE initiatives.
Institutions involved:
- UDA
- UNIOVI
- URN
- UOC
- XAMK
- HIS
- TUIASI
- MUS
- MTU
- HKA